Among the most advanced and complex technologies in medicine, implantable medical devices require careful design, production, and regulatory supervision to guarantee their safety and effectiveness. Their close proximity to the human body offers distinctive problems demanding rigorous restrictions. By means of the Medical Device Regulation (EU MDR), the European Union has built a solid foundation to improve the safety and performance of these essential products.
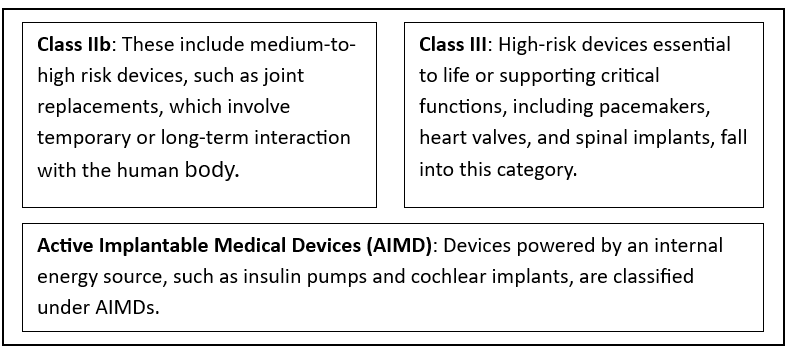
According to the EU MDR, implantable medical devices are classified as Active Implantable Medical Devices (AIMDs), Class IIb and Class III. This graded approach guarantees a level of review for items with different risk and complexity levels.
Manufacturers must perform thorough clinical studies proving the safety and effectiveness of their medical devices. This calls for producing strong clinical data from systematically conducted studies.
The EU MDR calls for a methodical and proactive PMS system to constantly track product performance following market introduction. This helps to spot and minimize possible safety concerns soon.
Implantable devices need to be given a unique identification number (UDI) to help quick identification and recall when safety concerns arise, therefore improving traceability and accountability. Stringent technical demands offers extensive technical instructions on many subjects including design and manufacturing techniques, biocompatibility testing, and risk management.
Regulatory Review and Compliance
Implantable devices must undergo a strict evaluation under the EU MDR. Manufacturers should work together with an EU-selected Notified Body for product assessment. This helps for a thorough analysis of technical reports, the Quality Management System (QMS), and clinical evidence. Notified Bodies audit companies and eventually issue CE approvals for market access.
Pivotal clinical assessments need strong data to show both efficacy and safety. Aligning results with legal standards depends partly on vital Comprehensive Clinical Evaluation Reports (CERs). Regarding ISO 14971, risk management is absolutely crucial. Encompassing elements including biocompatibility, general performance, and mechanical properties, manufacturers are mandated to early identify, assess, and alleviate risks all along the device life.
Obstacles and Best Practices
Though the EU MDR stresses safety and performance, several problems arise for producers. Particularly in the absence of competing goods, generating enough clinical evidence for new products might be difficult. Complex and time-consuming, compiling thorough technical information sometimes calls for contributions from engineers, medical specialists, and regulatory personnel. Moreover, the lack of Notified Bodies produces constraints that raise expenses and delay regulatory clearances.
To negotiate these issues, manufacturers should follow best practices:
Engagement early: Working with Notified Bodies in the development phase can help speed up regulatory paths and reduce delays.
For producing a solid evidence basis for submissions, it is essential to carry out meticulously designed clinical studies following ISO 14155 criteria.
Implementing an ISO 13485-compliant QMS guarantees throughout the life of the product effective control and verification of processes.
Using digital tools for PMS lets automate several types of work including incident reporting, trend analysis, and data acquisition, therefore improving accuracy and speed.
Expert collaboration in risk control, clinical appraisal, and cybersecurity enhances compliance tactics and raises regulatory reports.
Regulatory approaches for implantable medical devices under the EU MDR are crucial for ensuring patient safety, transparency, and global market access. The regulation emphasizes stricter clinical evidence requirements, robust biocompatibility evaluations, and enhanced traceability through UDI and EUDAMED. Future trends include greater reliance on real-world evidence and post-market clinical follow-ups (PMCF), alongside increasing regulation of smart, connected implantable integrating AI and addressing cybersecurity risks.
Sustainability is becoming a key focus, with eco-friendly materials and practices driven by the European Green Deal. The rise of personalized implants and 3D printing also calls for adaptive regulatory pathways. While these changes pose challenges such as higher costs and stricter evaluations, they offer opportunities to leverage innovative materials, real-time surveillance, and early collaboration with Notified Bodies. Staying aligned with these trends by investing in clinical data, enhancing post-market vigilance, and adopting sustainable practices will help manufacturers ensure compliance and drive innovation.
Conclusion:
Future regulatory guidelines should concentrate on improving the EU MDR even more on post-market monitoring and real-world evidence a rising application in real-world settings to track device performance and patient safety. Personalized Medicine: Adjustable channels for expediting the approval and creation of personalized equipment suited to unique patient needs. Strong security measures should be there to fight the changing issues of linked medical equipment, especially AIMDs.
Encouragement of international cooperation to standardize rules and ease market access would help to simplify the approval process for creative and low-risk products. Along with the creation of new biocompatible substances, they apply concepts of sustainability and environmental impact into device standards.
For implantable medical devices, the EU MDR has set a fresh standard of excellence, effectiveness, and safety. Complex as the regulatory environment is, companies using strategic planning, multidisciplinary cooperation, and strong compliance processes cannot just satisfy regulatory standards but also push healthcare innovation. Emphasizing patient safety and funding research and development, producers could negotiate the difficulties of the EU MDR and help advance life-changing medical technology.
Author- Shristi Ahir
Sr. Consultant, MDR Technical Expert